What is Cloud Computing?
Introduction to Cloud Technology
Introduction to Cloud Computing:
The National Institute of Standard and Technology (NIST) defines Cloud Computing as: “Cloud Computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (for an example, networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.”
Figure shows the pictorial representation
of Cloud Computing in details. Critical data that takes different forms, such
as emails, text documents, videos, chats and presentations are stored, accessed
and processed as needed by the cloud user – which is a set of software are
hardware devices (servers and storage) commissioned in a Data Centre, either in
a single or multiple locations.
Fig. Cloud Computing
Five Essential Characteristics of Cloud Computing:
1. On-demand self-service: Cloud Computing empowers the consumer to unilaterally provision computing capabilities like server time and network storage with no need for human interaction with individual service providers.
2. Broad network access: In Cloud Computing, the Internet allows any thin or thick client,
such as a laptop or a mobile phone, to access capabilities through standard
mechanism.
3. Resource pooling: In the cloud environment, the provider's computing resources are pooled
to serve multiple consumers through the multi-tenant model, with different
resources being assigned and reassigned on a real-time basis according to
consumer demand. The user loses control over the location of the data but many
be able to specify a higher level of abstraction.
4. Rapid elasticity: Capabilities can be both elastically and automatically provisioned and
released, to scale rapidly with demand to the consumers, the capabilities
available for provisioning often appear to be unlimited and can be appropriated
in any quantity at any time.
5. Measured service: Cloud systems automatically monitor, control, optimize and report
resource usage, thus providing transparency for both the provider and consumer
of the utilized services.
Three Service Models of Cloud Computing:
v
Software as a Service
(SaaS): The ability to access to provider's
applications running in the cloud environment is referred to as SaaS. Devices
such as smartphones, laptops, desktops and tablets can be used to access the
applications through a web browser or a program interface. The cloud user,
however, cannot access or manage the cloud infrastructure that hosts the
applications. This includes the servers, storage devices, network and
individual application components.
v
Platform as a Service
(PaaS): PaaS assists a developer who writes custom
application by provisioning the hardware, operating system (OS), database and
middleware. In the PaaS model, users do not have any control over the cloud
infrastructure just like the SaaS model. However, they have the ability to
monitor and manage the applications that they have deployed and the respective
configuration settings for application-hosting environment.
v
Infrastructure as a Service
(IaaS): The user is allowed to provision
processing, storage, network and other fundamental computing resources where
the consumer is able to deploy and run operating systems and other
applications. Through the cloud user can establish complete control over
operating systems, storage and deployed applications, the underlying cloud
infrastructure remains unperturbed.
Four Types of Cloud (Deployment Models):
NIST classifies the cloud into four different types as are:
1.
Private Cloud
2. Public Cloud
3. Hybrid Cloud
4. Community Cloud
History and Evolution of Cloud Computing:
History of Cloud Computing:
One of the most intriguing questions asked about Cloud Computing is "When and where was the first premise of Cloud Computing witnessed? “
The below section explains the growth of Cloud Computing over the last 50 years.
1950-1960:
The concept of time-sharing was introduced to allow multiple users to gain shared access to data and CPU time. This was done to lower the cost of maintenance of large-sized computers.
1960-1970:
ARPANET (Advanced Research Projects Agency
Network), the basis of internet was introduced. The basis of staying connected
and accessing data from any location was established.
1970-1980:
IBM introduced the Virtual Machine OS, and
this enabled users to have multiple virtual machines on a single physical node.
1980-1990:
The time period between 1980 and 1990
witnessed the emergence of Internet Service Providers and Application Service
Providers, which broke the realm of desktops and single user server to deliver
hosted applications services.
1990-2000:
The Internet became more prevalent, and
virtualized connections for PC-Based systems grew to connect network traffic
and bandwidth usage. Grid computing gained popularity along with
object-oriented programming and web services.
After 2000:
The 21st Century witnessed tremendous growth of the cloud as more and more corporate solutions and services from players like IBM and Oracle inundated the market.
Evolution of Cloud Computing:
The concept of virtualization emerged during the 1990s. Virtualization is the concept of creating logical computing resources (such as multiple servers) with limited physical resources (from a single physical server hardware available). It was then slowly expanded to virtual platforms that included storage and network resources.
Types of Cloud Computing
1. Private Cloud
Private Cloud allows systems and services to be accessible within an organization. The Private Cloud is operated only within a single organization.
2. Public Cloud
Public Cloud allows systems and services to be easily accessible to general public. The IT giants such as Google, Amazon and Microsoft offer cloud services via Internet. The Public Cloud Model is shown in the diagram below.
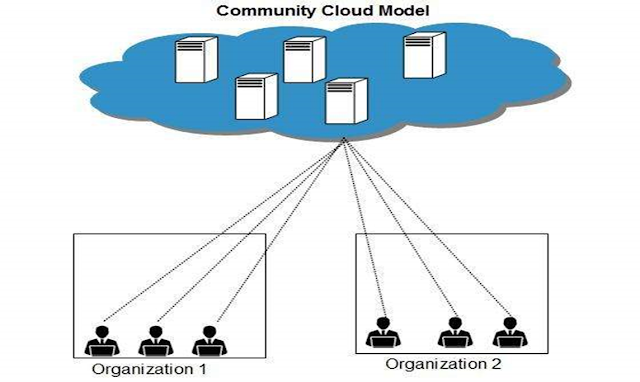
3. Community Cloud
Community Cloud allows system and services to be accessible by group of organizations. It shares the infrastructure between several organizations from a specific community.
4. Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid Cloud is a mixture of public and private cloud. Non-critical activities are performed using public cloud while the critical activities are performed using private cloud.
Cloud Computing Architecture:
Cloud Computing architecture comprises of
many cloud components, which are loosely coupled. We can broadly divide the
cloud architecture into two parts:
Ø
Front End
Ø
Back End
The following diagram shows the graphical view of cloud computing architecture:
1. Front End
The front end of the cloud architecture
refers to the client side of the system. It includes the network, applications
or programs that are used to access the cloud. For instance, while accessing a
web-based email application, the web browser acts as the front end.
2. Middleware
For smooth communication between the front
and the back end of the Cloud Computing Architecture, certain protocols must be
followed. The part of the system that connects the networked computers and
facilitates the proper functioning between the front and the back end is called
the middleware. It is a special software used by the central server to
administer the system.
3. Back End
The back end of the cloud architecture refers to the hardware section which includes the servers, deployment models, security mechanisms, storage and the computing systems. Based on the requirements, a specific hardware configuration is set up initially to get the organization into the cloud As the requirements increase, additional servers and storage modules are deployed from time-to-time.
1. Brief about Amazon Web Services:
Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers reliable and extensive cloud application and infrastructure services for all types of organizations. With over 10 years of experience in supporting enterprise with affordable cloud services AWS cloud has grown into a leader in cloud storage and management of various critical business processes.
Key things to know about AWS:
v
AWS is the pioneer in the Cloud
Computing race and has managed to retain its top position through the years.
v
Recent price cuts have allured
more startup as well as government agencies towards the AWS cloud.
v
Amazon offers three types of
computing instances: On-demand, reserved and spot. All three options come with
different pricing structures.
v
Amazon's cloud offering for Big
data analytics is called Amazon Elastic Map Reduce.
2. Brief about Microsoft Azure:
The enterprise-grade Cloud Computing platform from Microsoft is called Azure, and it supports a wide selection of tools, languages, frameworks, databases and devices. Statistics reveal that 57% of the Fortune 500 companies from various industry sectors entrust their data and application with Azure. The easy-to-implement and low-cost hybrid cloud solution offered by Microsoft Azure is a good fit for organizations of all types and sizes.
Ø More global regions than any other cloud provider:
Ø With the most global regions of any
cloud provider, Azure offers the scale you need to Bering your applications
Ø close to your users around the world.54regions 140countries
Ø More than 95 percent of Fortune 500 companies use Azure:
Ø Businesses and organizations around the
world - small and large, old and new - rely on Azure to provide
Ø trusted cloud services.
Ø 30+ years
Ø Over three decades of experience
serving enterprise customers.
Ø 68,000+ partners
Ø The industry's broadest and most
experienced partner network to support your needs.
Ø 70+ certifications
Ø The most comprehensive set of compliance offerings of any cloud service provider.
3. Brief about Google Cloud Platform:
The Google Cloud Platform allows users to build applications and store data on Google's highly reliable and scalable infrastructure. The innovation power of Google is world renowned, and by leveraging its cloud platform, developers can quicker access to its technological innovations.
Key things to know about Google Cloud Platform
- Google's network can be defined by its thousands of miles of
fiber optic cables connected through cutting-edge Andromeda networking.
The consistency and speed of such a network is unparalleled.
- Data is 100% secure through backup storage across multiple
locations.
- The per-minute billing system allows users to handle traffic
spikes with the most cost-effective solutions.
- The Big Query and Google Cloud Dataflow tools offer full
support to big data solutions.
The fact that
Google Cloud Platform works on the same infrastructure that support the mammoth
tasks of Google itself is indeed the greatest advantage. Users can be assured
of high availability.
4. Brief about IBM Cloud and Oracle Cloud:
IBM Cloud:
Cloud servers from IBM are designed for medium and large-sized enterprises that offer high-traffic and high demand solutions. IBM is quickly catching up with its competitors through offering a number of new products over the hybrid cloud at a reasonable pricing.
Oracle Cloud
Oracle is yet another cloud solutions provider joining the bandwagon with an exclusive portfolio of services for the IT development and infrastructure needs. The two major areas of focus while deploying cloud solutions from Oracle are- Innovation and Transformation. Oracle promises seamless integration of the cloud into the existing processes to transform them into sources of business efficiency and to open up several opportunities to derive innovation.
Merits and Applications of Cloud Computing:
Cloud Computing is
rapidly becoming a significant part of the overall IT strategy, and more and
more organizations are dedicating a substantial part of their IT budget towards
this trend. Cloud Computing is here to stay and deliver the following benefits:
Mobilizing the
workforce: Cloud Computing
allows device-agnostic access to data and access from any location. It breaks
all kinds of barriers and helps employees to stay connected on the move.
Increased cost
control: Cloud Computing saves
a lot of money by eliminating the need for upfront investment in infrastructure
and software. The pay-as-you-go model brings down operational costs and allows
higher efficiency.
Enhanced
productivity: Cloud allows
flexible provisioning of resources with the least impact on internal
operations. Personnel tend to focus better, and highly productive results can
be obtained.
Reduced impact on
the environment: With fewer
data centres and shared resources, enterprise moving to the cloud earn
eco-friendly credentials easily.
Better agility: While embracing cloud technology, organizations
can scale their resources up and down, avail automatic software updates and
expand exponentially with zero upfront investment and with out having to deal
with miles of wires and loads of servers.
Common Applications in the Cloud:
The last section
provided a clear outline on the various business benefits of Cloud Computing.
However, there exist certain data security and privacy issues while hosting
applications on the cloud. Organizations are widely experimenting with
different parts of the business that can yield favourable results without
falling victim to these concerns.
The most suitable and common applications that can be hosted in the cloud are:
v
Development
and Testing
v
Big Data
Analysis
v
Websites
and CRMs
v
Storage
and Backup
v
Disaster
Recovery
SUMMARY
Ø
Cloud
Computing refers to the delivery of computing resources and storage through the
internet on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Ø
The first
premise of Cloud Computing was witnessed in the early 1950s when CPU time was
shared among multiple users to cut down costs.
Ø
There are
four types of cloud delivery models: Private, Public, Hybrid and Community
cloud.
Ø
Provisioning
of infrastructure for controlled access by a single organization or providing
control access to restricted data and information for a new organizations in a
closed network format is referred to as private cloud.
Ø
When the
cloud resources are owned and managed by a third party and can be accessed by
all authorized users via the internet, it is called a public cloud.
Ø
The
solution that combines the best of both private and public clouds is called
hybrid cloud.
Ø
A
community cloud is a type of cloud primarily used by a closed group of people
or organizations. It is a collaborative effort, and the hardware infrastructure
is manually shared by two or more organizations from a specific community.
Ø
The cloud
architecture is made of three components: Front End, Middleware and Back End.
Ø
Some of
the most significant cloud service providers in the market today are AWS, IBM,
Oracle, Microsoft and Google.
Ø
Cloud
Computing has been widely adopted by organizations as it renders a number of
benefits such as cost efficiency, enhanced productivity and flexibility for the
business.

.png)




















ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon