Cloud Computing Delivery Models:
Topics:
1. Introduction.
2. Cloud Computing
Delivery Models.
3. Attributes of Cloud
Computing.
3.1 Virtualization.
3.2 Multi-tenancy.
3.3 Network Access.
3.4 Scalability.
3.5 Metering/Chargeback.
4. Software as a
Service (SaaS).
5. Platform as a
Service (PaaS).
6. Infrastructure as a
Service (IaaS).
7. Comparison of
Different Services.
8. Obstacles for Cloud
Technology
9. Cloud
Vulnerabilities
10. Cloud Challenges
11. Practical
Applications of Cloud Computing
12. Summary
Introduction
Cloud Computing is a
broad term that describes a broad range of services. Perhaps, that is the
reason there is no single, one-size-fits all definition for this term. Instead,
depending on what services one is describing or what you are talking to, the
moniker term 'cloud' is often described as a stack, as a response to the broad
range of services built on top of one another.
v
Definition
"Cloud Computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (for an example, network, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction."
Cloud Computing Delivery Models:
v Delivery models
v 1. Public cloud
v 2. Private cloud
v 3. Hybrid cloud
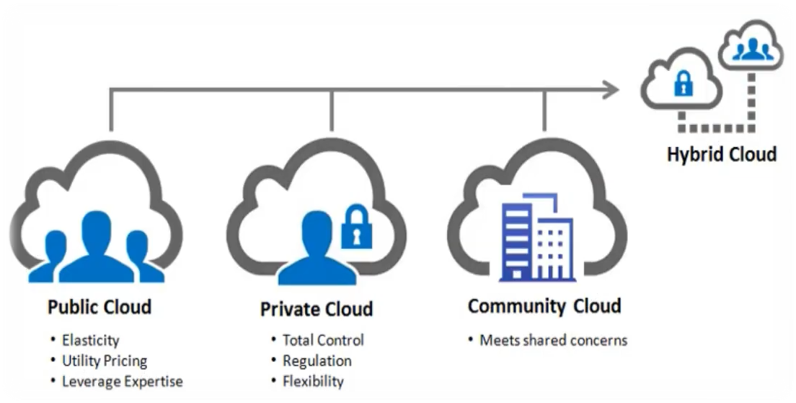
Public Cloud
•
This
utility model of Cloud Computing provides easy access to a shared
infrastructure, storages as well as other computing resources.
•
These
shared resources are hosted in a remote Data Centre, and multiple clients can
gain access to them using the internet.
•
Scalability and cost-effectiveness are
the major advantages
of a public cloud.
Private Cloud
Provisioning of
infrastructure for controlled access by a single organization providing
controlled access to restricted data and information for a new organizations in
a closed network format is referred to as private cloud.
All business units
within the organization can access the cloud without having to build their own
infrastructure.
Hybrid Cloud
As the name implies, a cloud that is a combination of two or more clouds (public cloud, private cloud or community cloud) is called as hybrid cloud. In a hybrid cloud environment, workloads can be moved between private and the public clouds based on changing computing needs and costs. This allows enhanced flexibility and more options when it comes to data deployment.
Community Cloud
•
A
community cloud is a type of cloud primarily used by a closed group of people
or organizations.
•
It is a collaborative efforts, and the
hardware infrastructure is mutually shared by two or more organizations from a
specific community.
•
It could either be managed or hosted
internally within an organizations in the community or by a third party cloud
service provider.
•
The infrastructure costs are shared among the
community members based on mutual agreements.
Attributes of Cloud Computing
When a company decides to move its one or more IT services to the cloud, it incurs many benefits, including lower capital costs, potentially lower operating costs, better support for mobile and remote personnel, and IT flexibility.
v Virtualization
Virtualization forms the core of cloud technology. It refers to the creation of virtual servers, memory, operating system or a storage device as opposed to the actual existence of the resource. In simpler terms, virtualization allows one physical computer to run several virtual machines at the same time.
v Multi-tenancy
Multi-tenancy, a key
common attribute of both private and public clouds, applies to all three
services of the cloud (SaaS, PaaS and IaaS). Consider an example of a cloud
service provider offering storage and backup solutions in the cloud.
Organizations that access these cloud resources are called tenants, and the
fact that many such tenants access these common resources gives rise to the
concept of multi-tenancy.
v Network Access
No cloud can exist
without a network. Network facilitate the sharing for resources, movement of
data and integrated functioning of the infrastructure components. The services
to be offered over the internet or private networks
are allowed by network access.
v Scalability
One of the strongest effects of Cloud Computing on a business is the scalability of IT resources. The business environment today suffers from increasing levels of unpredictability and shrinking IT budget.
v Metering/Chargeback
Metering or Chargeback
in the cloud ecosystem is the type of payment structure through which user can
gain unlimited access to all computing resources and yet pay for only their
actual usage. This allows the cutting down of excess costs that are usually
termed as IT overhead costs.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a
Service forms the base of the Cloud Computing stacks. The service offers the
ability to provision server, storage, networking and other basic computing
infrastructure resources through the internet and as required. Since the IaaS
cloud delivery model eliminates the need to invest in hardware, it is a perfect
solution for startup and for organizations that deal with extreme spikes and
troughs in usage.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS is the best fit
for organizations that are committed to the delivery of web and mobile applications within a
stipulated time and budget. A PaaS provider offers the toolkit to build an
application and the virtual machine to run it. Application developers can
design the functionalities as well as the interface based on their particular
needs.
Software as a Service (PaaS)
Software as a Service (SaaS) allows an organization to access the desired software applications through the cloud on a subscription basis. The SaaS vender offers access to the software applications with no upfront investment and takes care of all upgrades.
Comparison of Different Services
The "cloud" has become a universal buzzword, and all types of organizations are looking at driving the benefits of the cloud. The first step towards migrating to the cloud is to understand the three service-delivery models, their capabilities and limitations
Obstacles for Cloud Technology
Like with any other
technology, there are some significant obstacles to be overcome in cloud
computing too before it can turn into a part of the mainstream operations in an
organization. Common concerns that arise while choosing to adopt the cloud are:
v
Data
security and privacy issues: Moving
to the cloud means loss of control over applications an data to third party
provider, thus issues related to security and privacy are inevitable.
v
Adherence
to regulatory and compliance measures: Data in the cloud may be stored in a different location for better
performance and to avoid localised outages. In such cases, apart from the
industry-specific regulations, location-specific compliance measures must also
be met.
v
Vendor
lock-in: A robust SLA must be
established to avoid too much dependence on the cloud service provider.
v
Lack of
performance and uptime: Will
your application perform better in the cloud? Is your cloud service provider
promising the maximum uptime? These issues must be addressed before moving to
the cloud.
v
Network
connectivity and bandwidth:
Cloud Computing experts additional pressure on the internet used by the
organization, and bandwidth requirements must be evaluated based on the service
used.
v
Dependency
on outside agency: The
involvement of a third party into the internal operations of an enterprise may
sometime cause psychological obstacles for CIOs and IT managers.
v
Knowledge
and integration: Cloud
migration process must be done through a well structured procedure which will
be explained in detail in the upcoming chapters. With Cloud Computing, the IT
department must be prepared to embrace the changes in their roles and
responsibilities.
Cloud Vulnerabilities:
Cloud Vulnerabilities
can be defined as a weakness in any part of the cloud environment and can be
used by a potential attacker for personal gain. Some common Vulnerabilities
are:
v
Session
riding: When attackers use the
information form cookies to perform data theft or any similar cyber crime, it
is referred to as session riding. Tricking users into sending authenticated
requests to fake websites another form of this vulnerability.
v
Virtual
Machine Escape: Any vulnerability
in the hypervisor paves the way for potential attacks on the hypervisor as well
as for all virtual machines running on top of it. This vulnerability. though
rare, still exists and can causes serious damage in the worst cases.
v
Reliability
and Availability: Availability
of the cloud service directly translates to business value for the client.
However power outages, technical glitches and natural disasters are some common
sources that lead to cloud downtime.
v
Insecure
Cryptography: Cryptographic
algorithms used to generate random numbers must provide a large entropy pool
for maximum data protection. In the case of random number generators that offer
only a small entropy pool, easily guessable numbers could lead to security
issues.
v
Data
Portability: There may be
several reason for an organization to move its data from one cloud service
provider to another. Unsatisfying performance, finding a chapter option or the
cloud service provider running out of business could be some possible reason.
v
Vendor
Lock-in: Do you want to be
stuck with one single cloud service provider forever? The answer is definitely
not, given that the IT needs keep changing for every organization and another
provider in the industry may just come up with the most perfect solution for
your current needs.
v
Internet
Dependency: The internet is
the unsung hero of the entire cloud setup. An unfailing internet service
provider is what an organization needs to achieve 100% success in the cloud.
Cloud Challenges:
Once the decision to
embrace the cloud has been taken, organization must chart out a detailed plan
that marks their journey to the cloud. Listed below are the top challenges
battled in a cloud environment by the cloud vendor, client as well as the end
user.
v
Keeping
up with security requirements: Security
tops the list of challenges when it comes to Cloud Computing as organization
lose their direct control over data.
v
Obtaining
the right knowledge and expertise: With the advent of Cloud Computing, the role of the IT department has
significant changes and so has their need for knowledge and skills.
v
Choosing
the right vendor: Partnering
with the right vendor is the key to success in the cloud. Organizations must
follow a fail-safe mechanism in evaluating potential cloud vendors and ensure
that they meet all security and privacy standards.
v
Data
interoperability and portability: Organizations expand with time and their needs change rapidly.
Therefore, additional caution must be practiced to avoid choosing a
platform/technology/provider that makes the organization too dependent on them.
v
Budgeting
difficulties while moving to the cloud: The very nature of cloud is that it is scalable and is delivered on
demand. This, in turn, may cause difficulties while drawing IT budgets for that
entire organization.
Practical Applications of Cloud Computing:
v
Resource-hungry
applications: Applications
that demand many resources like the CPU, memory, storage or time can be hosted
on the cloud efficiently.
v
Application
with extreme spikes and troughs: Consider the example of an HR system that is accessed by employees only
a few times in a year. However, on the review day, every employees in the
organization logs onto the system thus slowing the system.
v
Special
Server Configuration: When
applications demand non-standard settings, the cloud server is a much easier
option to be configured to perfectly fit the requirements.
v
Backup
and Recovery: This is most
common application of cloud as it is clearly more expensive to manage the
entire duplicate infrastructure.
Summary:
ü
The three
categories of cloud services, Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a
Service (PaaS) and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) together form the Cloud
Computing stack.
ü
Software
as a Service (SaaS) allows an organization to access the desired software
applications through the cloud on a subscription basis.
ü
The PaaS
model of Cloud Computing enables organization to access the toolkit to build
the software application and the virtual machine to run it.
ü
IaaS is
the ability to provision server, storage, networking and other basic computing
resources through the internet as and when required.
ü
The key
attributes of a Cloud Computing environment are virtualization, multi-tenancy,
networking access scalability and metering/chargeback.
ü
Implementing
the cloud paves the way for some challenges like privacy and security concerns,
low quality of service, and loss of control and so on. The key lies in choosing
a reliable cloud service vendor and establishing strong SLAs.
ü
Though all
kinds of web applications can be hosted on the cloud, applications with special
server configuration, varying levels of utilization and resources-hungry
application are the most suitable candidates for the cloud.
ü
ICICI
Lombard, WhatsApp and Expedia are great stories that exemplify the power of
cloud in today's business world.

.png)













ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon